Regulation of alternative splicing, RNA processing & gene expression by hnRNP L
...we are investigating the functions and implications of the multifunctional RNA-binding protein hnRNP L
The multifunctional RNA-binding protein hnRNP L is involved of many aspects of RNA processing. It is ubiquitously expressed, highly abundant and binds to CA-repeat and CA-rich sequences on pre-mRNA in the nucleus. It has been implicated in the regulation of many different processes, such as mRNA stability, RNA export, alternative polyadenylation and alternative pre-mRNA splicing where it can act as an activator or repressor. It has been shown to interact with many non-coding RNAs, and to thereby play a role in inflammation. It is a component of the KMT3a-complex and is involved in Histone H3K36 methylation. It competes with microRNA binding in the 3’-UTRs of several mRNAs. An especially interesting case of this mechanism is its competition with microRNAs-297 and -299 in hypoxia.
Under normal conditions, the VEGFA (vascular endothelial growth factor A) mRNA translation is repressed by these microRNAs. Interestingly, under hypoxic conditions (occurring in tumors or cardiovascular disease) hnRNP L, which is mainly localized in the nucleus, is relocated to the cytoplasm. Here it binds to the VEGFA 3’-UTR in the same region as the abovementioned microRNAs and thereby de-represses VEGFA translation. Expression of this growth factor then leads to vascularization of the hypoxic tissue. This mechanism is an interesting target for drug development in cancer and cardiovascular disease.
Our group is interested in different aspects of hnRNP L-mediated regulation: we have investigated alternative splicing regulation by hnRNP L, and thereby uncovered a negative feedback loop by which hnRNP L regulates its own expression (see Figure above). This involves a highly conserved splicing enhancer binding site in its own pre-mRNA that is bound by the protein. This leads to incorporation of an exon which contains a premature termination codon and thereby triggers degradation of the mRNA by nonsense-mediated decay. This mechanism regulates hnRNP L proteins levels in the cell.
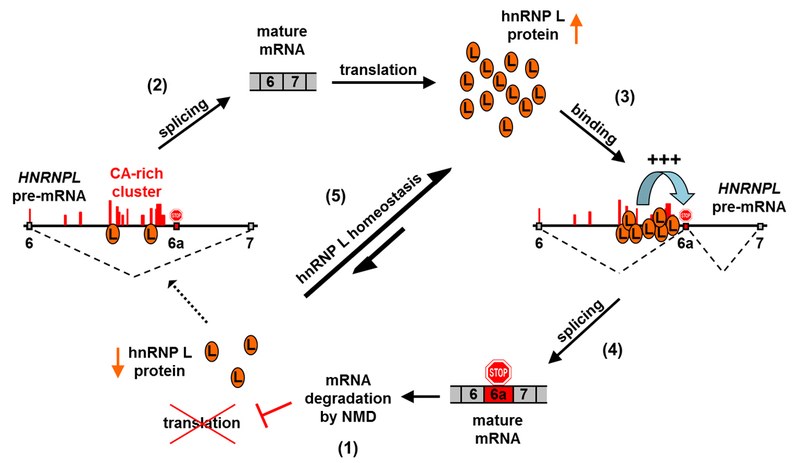
We have performed iCLIP with hnRNP L and uncovered a positional code of its splicing regulation, a novel function in snoRNA biogenesis and a transcriptome-wide competition with microRNA binding, exceeding the VEGFA case that had been reported before. We are now aiming to uncover other functions of hnRNP L in disease-relevant conditions, such as hypoxia, and systematically analyze the mechanism that govern hnRNP L re-location and its roles in the cytoplasm.
-
Müller-McNicoll M, Rossbach O, Hui J, Medenbach J. Auto-regulatory feedback by RNA-binding proteins. Journal of Molecular Cell Biology. 2019 Jun 1. pii: mjz043. (Article Link)
-
Rossbach O, Hung LH, Khrameeva E, Schreiner S, König J, Curk T, Zupan B, Ule J, Gelfand MS, Bindereif A. Crosslinking-immunoprecipitation (iCLIP) analysis reveals global regulatory roles of hnRNP L. RNA Biology. 2014 Feb; 11(2):146-55. (Article Link)
-
Rossbach O*, Hung LH*, Schreiner S*, Grishina I, Heiner M, Hui J, Bindereif A. Auto- and cross-regulation of the hnRNP L proteins by alternative splicing. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2009 Mar; 29(6):1442-51. (Article Link)
-----
(* these authors contributed equally)
