Photochemistry of HNSO2 in Cryogenic Matrices: Spectroscopic Identification of the Intermediates and Mechanism
Changyun Chen, Lina Wang, Xiaofang Zhao, Zhuang Wu, Bastian Bernhardt, André K. Eckhardt, Peter R. Schreiner, Xiaoqing Zeng
PCCP 2020, 22, 7975–7983. DOI: 10.1039/D0CP00962H
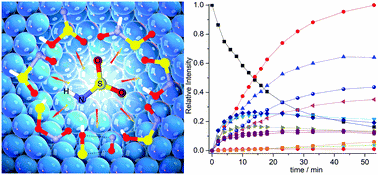
Small molecules solely consisting of H, N, O, and S are highly relevant intermediates in atmospheric chemistry and biology. Even though several isomers of [HNO2S] have been computationally predicted, only the IR spectra for the two lowest-energy isomers HNSO2 and syn–syn HONSO have been previously reported. Herein, the photochemistry (193 nm laser) of HNSO2 in N2-, Ne-, and Ar-matrices (≤15 K) has been studied. Aside from syn–syn HONSO, several new isomers including anti–syn HONSO, gauche–syn HOSNO, syn HOS(O)N, anti HOS(O)N, syn HS(O)NO, anti HN(O)SO, gauche–syn HSONO, and an elusive caged-radical pair HOS˙⋯˙NO have been identified. Additionally, the formation of fragments HONO, HO˙, ˙NO, and ˙NO2 has also been observed. The characterization of these species with matrix-isolation IR and UV/Vis spectroscopy is supported by 15N-labeling and quantum chemical computations at the B3LYP/6-311++G(3df,3pd) level. Furthermore, the photo-induced isomerization reactions, including the conformational conversion of syn–syn HONSO → anti–syn HONSO and reversible isomerization of HOSNO ↔ anti–syn HONSO, syn–syn HONSO ↔ HN(O)SO, HSONO ↔ HS(O)NO, and HOS˙⋯˙NO ↔ HOSNO have also been observed, and the underlying mechanism is discussed.