B05
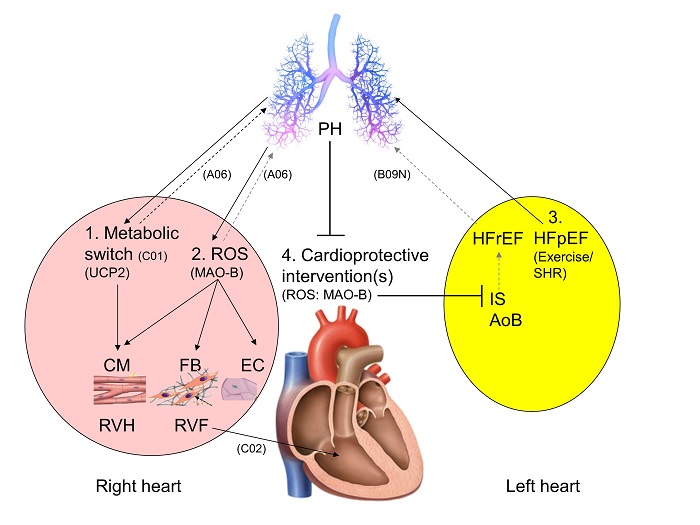
Importance of mitochondrial ROS and substrate metabolism for the development and progression of right heart failure
Right ventricular (RV) failure during pulmonary hypertension (PH) is associated with an increase in reactive oxygen species (ROS) and a metabolic switch. In isolated rat cardiomyocytes, this metabolic switch causes dysfunction which will be validated in vivo in PH rats. Blocking the small mitochondrial p66shc-induced ROS increase in PH rats did not improve RV function but affected morphology. Whether this is true for blocking the bigger monoaminooxidase B-induced ROS increase is under investigation. In systems of PH induced by left heart failure.