Teilprojekt 6 - Interventionsstudien beim Menschen
Bioverfügbarkeits- und Interventionsstudien beim Menschen
Workpackage 6:
Human bioavailability - and intervention studies
Project team: Prof. Dr. C. Kunz, G. Abel, Dr. C. Borsch, Dr. S. Kuntz, Prof. Dr. S. Rudloff, Prof. Dr. R. G. Bretzel, FB 09 und FB 11, JLU
Email: clemens.kunz@uni-giessen.de
Background
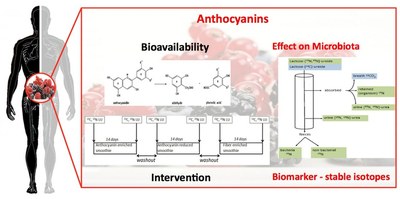
In the bioavailability and intervention studies metabolic aspects and the effects of anthocyanins in humans. will be investigated.
Although there have been numerous in vitro-studies, proving the positive value of different anthocyanins the clear assessment of their effectiveness in humans is very difficult. One reason for this is that in many studies the effects of single components have often been tested in high concentrations; hence, without physiological relevance .
Apart from that those substances are subject to a distinctive microbial fermentation in the gastrointestinal tract as well as an intestinal metabolism.
While in our studies on the bioavailability the focus is put on type and quantity of anthocyanins and metabolites in biological fluids the intervention study primarily examines the effects on anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory processes as well as the composition and metabolic functions of the microbiota. Thereby, one aspect is the establishment of new biomarkers for the effectiveness by using stabile isotopes.
In this project a close direct collaboration with projects 1,2, 3 and 4 is given. Stabile isotope studies are carried out in project 4 within the “Method Platform – Stabile Isotopes and Cell Biology” (http://www.methodenplattform.de/).
Aims
The aims of this project are (1) to analyse the bioavailability of anthocyanins derived from innovative berry-fruit juices in humans; (2) to determine the influence on composition and metabolic function of the microbiota within an intervention study and (3) to establish new biomarkers while using stable isotopes as an innovative approach to examine metabolic functions.