Research
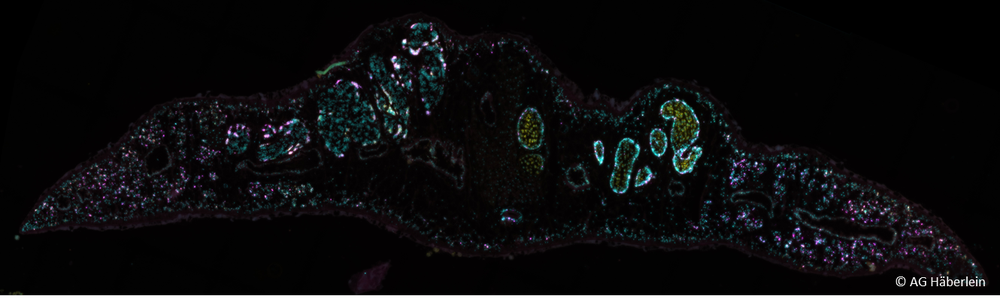
Our projects address various fascinating aspects of the molecular biology of liver flukes and schistosomes. These include the study of their stem cell biology, the generation of a cell atlas and spatial gene expression map, the characterization of the kinome, and the measurement of biophysical properties. A major goal is to find new molecular targets to combat the parasites. We focus on protein kinases, transcription factors, RNA binding proteins, calcium channels and cellular processes such as autophagy and mechanotransduction.
As part of our drug discovery funded by the LOEWE center DRUID, we perform in vitro screening of test compounds against the parasites. With cooperation partners from chemistry and the Fraunhofer Institute, we identify natural compounds with antiparasitic activity.
Our projects
 |
Transcriptomics in FasciolaClassical RNA-seq methods have low cellular resolution. Here we apply "cutting edge" methods for improved resolution in F. hepatica
This take place in two different projects |
 |
Physics in HelminthsThis project will investigate fundamental biomechanical principles that contribute to parasite adhesion, locomotion, and reproduction. |
 |
Kinome AnalysisKinases play a key role in many biological processes, due to their central role they are an interesting target for new treatment strategies. Therefore, we are working on the identification of kinases in the F. hepatica genome.
|
 |
Development of alternative treatments
Diseases caused by helminths affect the health of many people worldwide. As part of the DRUID research center, this project tests and evaluates compounds to find new treatment options.
|
|
|
|
||
 |
RNAi as treatmentThe aim is to establish the basis for a new form of treatment against schistosomiasis using RNAi therapy. In doing so, we interfere with the expression of vital genes of the pathogen.
|
|
