A10N
Inflammatory lung microenvironment in lung cancer-associated pulmonary hypertension
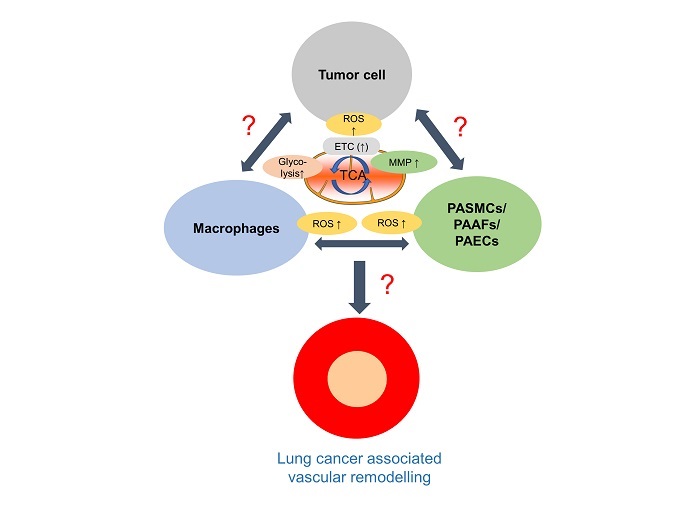
Lung cancer (LC) is one of the major causes of mortality and morbidity worldwide. We recently showed that lung cancer induces pulmonary vascular remodeling leading to pulmonary hypertension (LC-PH). Innate immune cells predominate in the lung tumor microenvironment, among which tumor associated macrophages (TAMs) have been shown by us to significantly contribute to the pathogenesis of both LC and LC-PH. We thus aim to decipher the role of macrophages in development of LC-PH and the signaling pathways underlying the crosstalk between tumor cells, macrophages and vascular cells. Thereby, a novel macrophage specific and cell-based immunomodulatory therapeutic approach for LC-PH should be developed.