Non-coding RNAs for crop protection
Karl-Heinz Kogel, Patrick Schäfer
Subprojects:
Non-coding RNA application and uptake mechanisms – Maria Ladera-Carmona
Role of non-coding RNAs in beneficial symbioses – Ena Šečić, Jens Steinbrenner
Cross-kingdom RNAi in in pathogen control – Bernhard Timo Werner
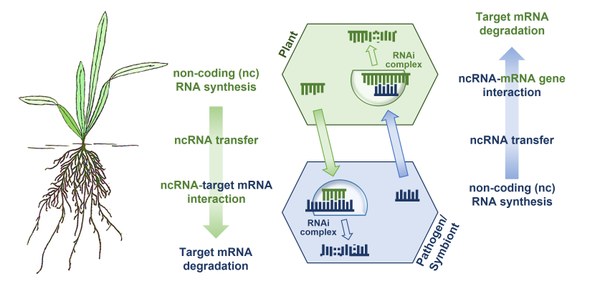
Background: The regulation of fundamental processes in plants and eukaryotic microbes involves non-coding (nc) RNAs. While underlying processes are well-known to regulate different aspects in plant and microbial development, their importance in beneficial and pathogenic plant-microbe interactions has just started to be recognised. Plant microbes release ncRNAs to manipulate mRNAs and gene activity in host plants that would interfere with their colonisation (e.g. defence genes). Plants, in turn, deliver ncRNAs into microbes as part of their defence system and microbes are amenable for plant ncRNAs. This phenomenon, termed bidirectional RNA communication or cross kingdom RNAi (ckRNAi), indicates the importance of RNAi processes in the regulation of disease resistance and the establishment of beneficial symbioses. The plant RNA interference (RNAi) machinery includes families of RNA-DEPENDENT RNA POLYMERASE, DICER-LIKE and ARGONAUTE genes that are involved in the production of ncRNAs. Our aim is to identify the function of ncRNAs and RNAi genes in disease resistance and symbiont-mediated crop protection.
Project: We aim at finding novel RNAi-based resistance mechanisms against plant diseases. To deepen our understanding of underlying resistance mechanisms and to facilitate the rapid application of the gained knowledge (e.g. in breeding programmes) we combine model and crop plants, lab and field studies, natural diversity screens, functional genetics and comparative omics. Focusing on different pathogens as well as resistance-inducing beneficial microbes will help to identify more durable and preferably conserved resistance traits in plants. In addition, studying ncRNA import/export mechanisms will assist us not only in identifying principles of cross-kingdom ncRNA exchange but to develop solutions for the effective application of ncRNA-based strategies in crop protection.
Lab tools / techniques: ckRNAi-seq, comparative epigenomics, ncRNA assays, host-/spray-induced gene silencing.