Demarcation and protection of heterochromatin domains
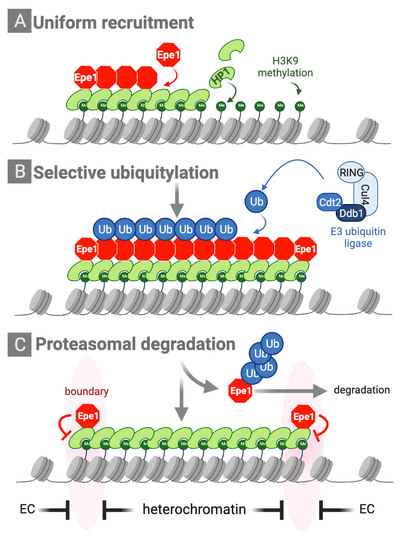
Partitioning into active and silent chromatin requires dedicated mechanisms that specify boundaries and maintain the identity of chromatin domains. We previously discovered a novel mechanism by which the distribution of an anti-silencing factor within heterochromatin is shaped through ubiquitin-dependent protein degradation. This mechanisms we coined ‘chromatin sculpting’ is essential for the establishment of chromatin boundaries and the protection of heterochromatin inside (Braun et al., Cell 2011). The integrity of chromatin domains can also be maintained through anchoring of factors and histone-modifying enzymes to specific chromatin regions, thereby preventing their promiscuous binding to other parts of the genome. In collaboration with Marc Bühler’s lab, we showed that the histone-methyl reader Pdp3 recruits the acetyltransferase Mst2 to euchromatin via recognition of methylated H3K36, a histone mark of actively transcribed chromatin. This anchoring mechanisms prevents Mst2 from encroaching heterochromatin and triggering a silencing defect (Flury et al., Mol Cell 2017; Georgescu et al., Microbial Cell 2020).