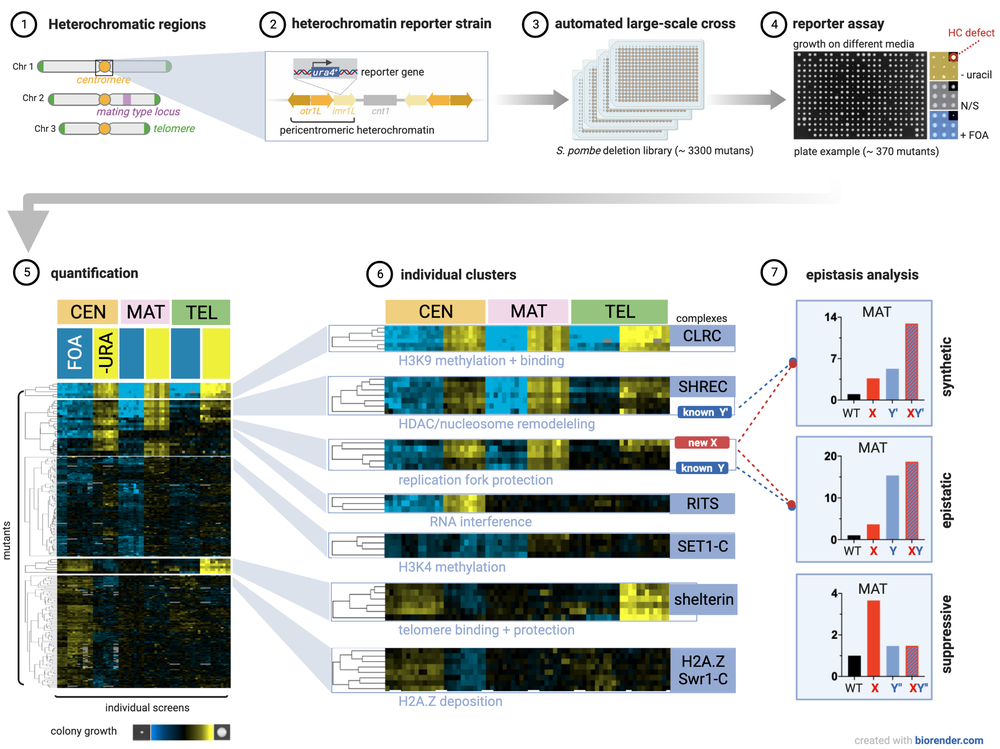
Identifying novel factors and dissecting regulatory networks
By employing automated genome-wide screens and monitoring silencing at all major heterochromatin domains in S. pombe, we have identified a large number of factors that modulate the silent state of these domains. To understand the roles of these novel factors in heterochromatin regulation, we assign them to functional pathways by systematically analyzing their genetic interactions using the SGA (Synthetic Gene Arrays) approach. This allows us to dissect factors acting within the same pathway displaying non-additive phenotypes from factors of parallel pathways exhibiting synthetic phenotypes (Verrier et al., Open Biol 2015; Barrales et al., Genes Dev 2016; Flury et al., Mol Cell 2017; Salas-Pino et al., JCB 2017). Future work aims on assessing systematically the pair-wise genetic interactions of all identified factors by an advanced version of the E-MAP (Epistasis Mini-Array Profile) approach. Beyond, we seek to examine the impact of environmental cues and stress on heterochromatin regulation.